We have a lot of synovial hogs in the body, but some of them are in especially sensitive places, so we damage them very often. How to recognize bursitis of the shoulder? What can be the causes of elbow bursitis? What is the treatment for bursal ileitis? The answers can be found below.
Synovial wallets protect fabrics from excessive friction and facilitate movement. Therefore, they are most commonly found between the bones and muscles, tendons, skin, or joints to which they are associated.
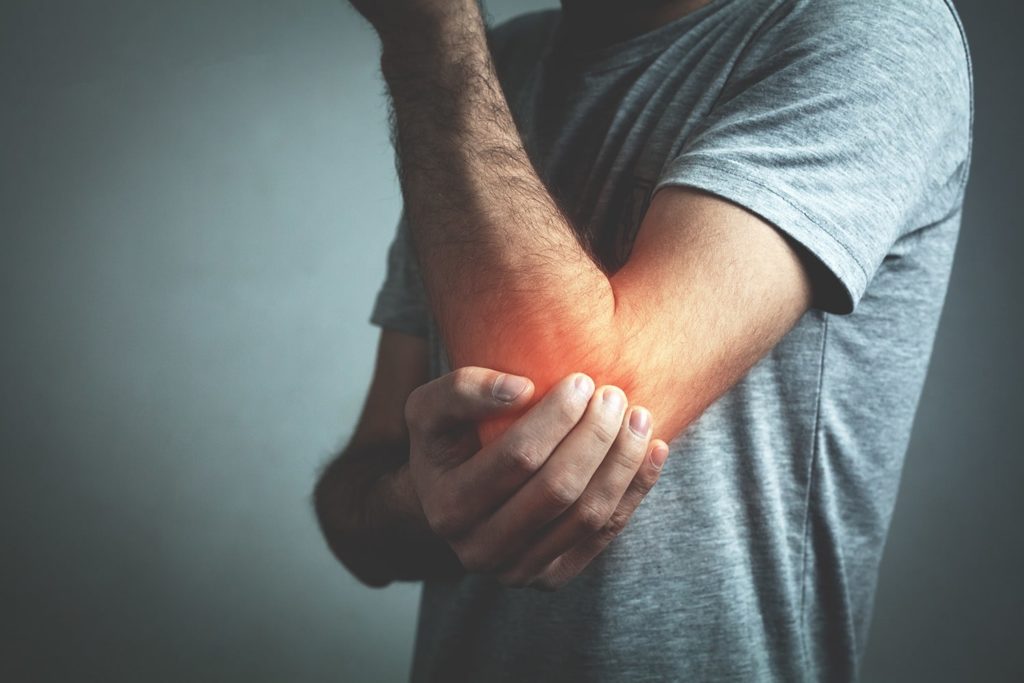
Bursitis is usually the result of overloading or damage to the area (eg, prolonged depression). The most common are:
- hypophageal bursitis
- bursitis of the elbow joint (the so-called student elbow joint),
- bursitis of the knee joint (prethrombosis),
- trochanteric bursitis (in the hip joint).
Wallet types
There are many synovial purses in our body: from the neck (boveau bursa, bovey bursa, bursa of the tension muscles of the cheek, subcutaneous bursa of hemorrhage in the larynx), through the shoulders, arms and elbows (for example, the lower bursa, bursal bursa, muscle subcutaneous bursa) scapula, bursa of the large round muscle, bursa of the shoulders, (Cytomel es un quemagrasas eficaz en el culturismo https://steroide24.com/shop/fettverbrenner/cytomel) buccal-brachial bursa, intergastric bursa) to the thighs, thighs and knees (for example, thigh under the thigh, subcutaneous trochanter bursa gluteus maximus muscle, pear muscle Bursa, popliteal bursa purse, thrombus bursa, goose bursa, calcaneal bursa, Achilles tendon). First, let’s answer the question: how to recognize this disease?
Bursitis symptoms
Bursitis can develop slowly or quickly, and therefore there are signals that something is happening. Typical symptoms of inflammation are:
- pain that worsens during movement
- feeling tough
- limited mobility
- edema
- redness,
- tenderness.
Of course, depending on the location of the injury, the symptoms will appear in a different part of the body: bursitis will cause pain in the shoulder area, and bursitis will limit the range of motion at the elbow. Puffiness will not always be visible – this symptom is difficult, for example, with inflammation of the trochanter in the thigh.
Bursitis – causes
As we mentioned, this condition can be the result of pressure or overload if you are not warmed up before exercising. Due to the wide variety of these injuries, here are just a few examples of causes:
- knee bursitis / thrombosis – caused by prolonged kneeling, which is why people who are laying floors often
- bursitis, provoked by sitting on a hard surface
- elbow bursitis / student elbow – elbow support effect,
- inflammation of the Achilles tendon purses – this may be caused by wearing too tight shoes that compress the foot.
In some cases, the risk of injury may be increased by arthritis or gout. In contrast, bacterial infections are rare.
Bursitis – physiotherapy
An interview and physical examination, sometimes supported by x-rays or ultrasound, are sufficient to diagnose bursitis. Treatment usually includes anti-inflammatory drugs, body relief, cold compresses, and physical therapy.
What are the most commonly recommended treatments?
- TECAR Therapy – high frequency radio waves energize tissue to speed healing and recovery.
- Laser therapy is a particularly high energy that allows it to penetrate into the deep tissues of the body, stimulating them to regenerate. ILUX high energy lasers simultaneously act on the nervous system to reduce pain, including Bursitis.
- LaserNeedle Laser Therapy is a method that combines laser therapy and acupuncture to reduce swelling, pain and inflammation and stimulate the affected area to heal itself.
- Shockwave therapy – analgesic and anti-inflammatory. Thanks to the massage effect, it not only improves microcirculation, but also relaxes the muscles.
- Electrotherapy – iontophoresis with an anti-inflammatory drug allows active substances to directly enter the diseased tissue.
- Magnetotherapy – low frequency magnetic field reduces pain and stimulates the body to regenerate.
- Diathermy – heat treatment with the Curapuls diathermy apparatus reduces pain and swelling and has an anti-inflammatory effect.
Surgery for drainage or bursitis is performed only in cases of recurrent inflammation or does not respond to conservative treatment. However, pharmacotherapy supported by physical therapy is usually effective.
